Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing - If there is little space between protein fibers, the tissue is likely one of the dense connective tissues. These serve to hold organs and other tissues in place and, in the case of adipose tissue, isolate and store energy reserves. Web reticular fibers are abundant in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen), bone marrow and liver. Produce stroma that supports other cells in lymphoid organs. Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. Reticular fibers are attached to reticular cells; Web reticular tissue is a special type of connective tissue that predominates in various locations that have a high cellular content. Reticular fibers (type iii collagen) are too thin to stain in ordinary histological preparations, but they are. Lymph node, silver stain iowa virtual slidebox: Form a tightly woven fabric that joins connective tissue to adjacent tissues. The cells that make the reticular fibers are fibroblasts called reticular cells. Reticular fibers are composed of thin and delicately woven strands of type iii collagen. Web reticular connective tissue, 40x. The specific types and relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance determine the overall structure and function of connective tissues. These serve to hold organs and other tissues. The units that together form these fibers are called reticular cells or fibroblasts. Web reticular tissue is a specific form of connective tissue predominating in several regions with high cellular content. Reticular connective tissue forms a scaffolding for other cells in several organs, such as lymph nodes and bone marrow. Web reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in. Reticular connective tissue forms a scaffolding for other cells in several organs, such as lymph nodes and bone marrow. Web reticular tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with an extracellular matrix consisting of an interwoven network of reticular fibers that provide a strong yet somewhat flexible framework (known as the stroma) for other types of functional cells to. The specific types and relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance determine the overall structure and function of connective tissues. Fine fibers • offer strength & support; Web reticular tissue is a special type of connective tissue that predominates in various locations that have a high cellular content. • “packing material” of body (fill space / cushion / stabilize. Reticular connective tissue is a type of connective tissue [1] with a network of reticular fibers, made of type iii collagen [2] ( reticulum = net or network). Drawing activityon a blank piece of paper draw the components of reticular connective tissue, including fibers and cell types.enter the important histological characteristics of reticular connective tissue into the table.make sure you. These soft organs need an internal scaffolding called the. Web reticular connective tissue 10x. The skin is composed of two main layers: Function of reticular connective tissue. Web reticular tissue is a specific form of connective tissue predominating in several regions with high cellular content. Lymph node, silver stain (175) examine this slide at low and medium (~24x) power to see the outer connective tissue capsule surrounding this lymph node, as well as trabeculae that invaginate into the node and provide it with structure. Web reticular connective tissue, 40x. Drawing activityon a blank piece of paper draw the components of reticular connective tissue, including fibers. Web the major types of connective tissue are connective tissue proper, supportive tissue, and fluid tissue. Further divided into loose and dense connective tissues; Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this type they are dominant. • “packing material” of body (fill space / cushion / stabilize / support) chapter 4: Other types of white. Web connective tissue • comprises cells suspended in an extracellular matrix of protein fibers and ground substance. This tissue must be specifically stained and is usually taken from a lymph node or the spleen. Produce stroma that supports other cells in lymphoid organs. The skin is composed of two main layers: Comprises an abundance of reticular fibers that form complicated. These fibers are made up of collagen and glycoproteins. Loose connective tissue proper includes adipose tissue, areolar tissue, and reticular tissue. These are specialized fibroblasts that synthesize and hold the fibers. Further divided into loose and dense connective tissues; Web categorized under loose connective tissues, reticular connective tissues are also named as reticular fibers, which are an essential part of. Forms stroma of liver, spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. Web connective tissue • comprises cells suspended in an extracellular matrix of protein fibers and ground substance. The units that together form these fibers are called reticular cells or fibroblasts. Reticular fibers are composed of thin and delicately woven strands of type iii collagen. We know that there are way cooler histology topics than connective tissue, like muscle tissue or neural tissue. These fibers are actually type iii collagen fibrils. These soft organs need an internal scaffolding called the. These serve to hold organs and other tissues in place and, in the case of adipose tissue, isolate and store energy reserves. Function of reticular connective tissue. Other types of white blood cells are also typically present. Web the major types of connective tissue are connective tissue proper, supportive tissue, and fluid tissue. Web connective tissue proper; Tissues types of connective tissue: Occupied primarily by collagen fibers 1) connective tissue proper: Loose connective tissue proper includes adipose tissue, areolar tissue, and reticular tissue. Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this type they are dominant.
Connective Tissue Supports and Protects · Anatomy and Physiology

Reticular connective tissue cells and structure (preview) Human

chapter 4 connective tissues neuron stuff and other science stuff

Reticular Connective Tissue, 40X Histology

Reticular Connective Tissue Labeled

Reticular Connective Tissue Structure

Connective Tissue Reticular cross section magnification… Flickr
Reticular Connective Tissue 20x Histology

Reticular connective tissue Microscopic cells, Loose connective
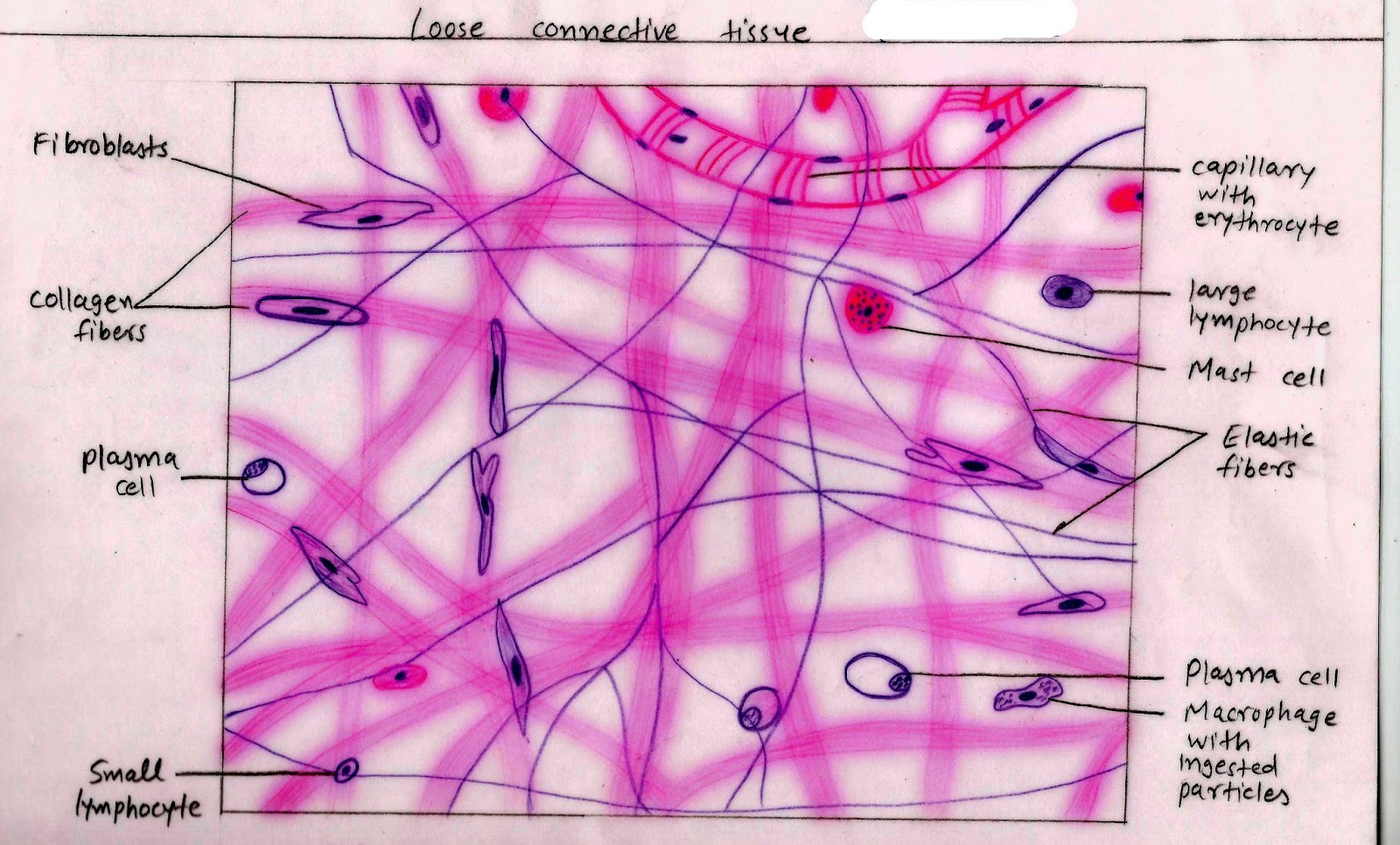
Histology Image Connective tissue
Fibers Made Of Collagen Fibers That Are Very Thin And Branched.
These Fibers Are Made Up Of Collagen And Glycoproteins.
Comprises An Abundance Of Reticular Fibers That Form Complicated Branching And Interweaving Patterns.
This Tissue Must Be Specifically Stained And Is Usually Taken From A Lymph Node Or The Spleen.
Related Post: