Enzyme Drawing
Enzyme Drawing - Enzymes are specific to the substrate they interact with. This sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is called the primary structure. Inject a dose of either agent into the recipient, follow it an hour or two later with a blood draw and, they hoped, the haystack would contain a lot more needles for a liquid biopsy to find. Web chemdraw isn’t limited to drawing chemical structures. The tool can be utilized by any interested researcher for efficient testing and evaluation of various kinetic models for a. Web tips on drawing enzymes and substrates quality 1080p 720p 480p 360p 240p 1080p 720p 480p 360p 240p 192p 1080p 720p 480p 360p 240p speed 0.5 0.75 normal 1.25 1.5 Web an enzyme marker test is a simple blood draw. Web the set of amino acids found in the active site, along with their positions in 3d space, give the active site a very specific size, shape, and chemical behavior. Web enzymes are biocatalysts, which are high molecular weight proteinous compounds. It helps the substrate by providing the surface for the reaction to occur. The total number of different enzymes in the biosphere must be staggering. Web enzymes are proteins comprised of amino acids linked together in one or more polypeptide chains. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body. The tool can be utilized by any interested researcher for efficient testing and evaluation of various kinetic models for a. Web. Inject a dose of either agent into the recipient, follow it an hour or two later with a blood draw and, they hoped, the haystack would contain a lot more needles for a liquid biopsy to find. Enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. Web enzymes and other catalysts decrease the activation energy required to initiate a. It regulates cell chemistry so that the proper reactions occur in the proper place at the proper time. Schematic drawing of an enzyme reacting with its substrate. Speed is key when it comes to effective freezing, and. The enormous catalytic activity of enzymes can perhaps best be expressed by a constant, k cat, that is variously referred to as the. Web enzyme specificity results from the uniqueness of the active site in each different enzyme because of the identity, charge, and spatial orientation of the functional groups located there. Second, draw in and label the appropriate interactions between the r groups and the substrate. It regulates cell chemistry so that the proper reactions occur in the proper place at the. The secondary structure of a protein describes the. Web introduction to enzymes mechanisms. A phlebotomist (a specialist trained in drawing blood) or another healthcare provider draws your blood. Enzymes are specific to the substrate they interact with. The human genome encodes for over 20,000 different proteins, thousands of which are enzymes. Speed is key when it comes to effective freezing, and. It regulates cell chemistry so that the proper reactions occur in the proper place at the proper time. Once the reaction is completed, the reaction products are released from the active site of the enzyme. Explain how these interactions might change if the ph of. The total number of different. Speed is key when it comes to effective freezing, and. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein enzymes. Web introduction to enzymes mechanisms. The secondary structure of a protein describes the. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body. The single most important property of enzymes is the ability to increase the rates of reactions occurring in living organisms, a property known as catalytic activity. Web enzyme kinetics graph showing rate of reaction as a function of substrate concentration for normal enzyme, enzyme with a competitive inhibitor, and enzyme with a noncompetitive inhibitor. Web an enzyme exhibits maximum activity. Web i’ve found that even my freshman can grasp the basic concepts of enzymes, substrates and activation energy. Web enzymes are the catalysts involved in biological chemical reactions. Catalysts bring reactants closer together in the appropriate orientation and weaken bonds, increasing the reaction rate. A catalyst is a chemical involved in, but not consumed in, a chemical reaction. It regulates. A catalyst is a chemical involved in, but not consumed in, a chemical reaction. It enhances the reactions which occur in the body during various life processes. Web tips on drawing enzymes and substrates quality 1080p 720p 480p 360p 240p 1080p 720p 480p 360p 240p 192p 1080p 720p 480p 360p 240p speed 0.5 0.75 normal 1.25 1.5 The median value. Web the set of amino acids found in the active site, along with their positions in 3d space, give the active site a very specific size, shape, and chemical behavior. A catalyst is a chemical involved in, but not consumed in, a chemical reaction. Web enzymes are proteins comprised of amino acids linked together in one or more polypeptide chains. Speed is key when it comes to effective freezing, and. Enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. For the competitive inhibitor, vmax is the same as for the normal enzyme, but km is. With the notable exception of gastric juice (the fluids secreted in the stomach), most body fluids have ph values. Without an enzyme (left), the energy input needed for a reaction to begin is high. Web enzyme kinetics graph showing rate of reaction as a function of substrate concentration for normal enzyme, enzyme with a competitive inhibitor, and enzyme with a noncompetitive inhibitor. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein enzymes. The procedure takes only a few minutes. Inject a dose of either agent into the recipient, follow it an hour or two later with a blood draw and, they hoped, the haystack would contain a lot more needles for a liquid biopsy to find. The total number of different enzymes in the biosphere must be staggering. Thanks to these amino acids, an enzyme's active site is uniquely suited to bind to a particular target—the enzyme's substrate or substrates—and help them undergo a chemical reaction. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body. Enzo is a web tool for easy construction and quick testing of kinetic models of enzyme catalyzed reactions.
Enzyme vector illustration. Full labeled cycle and diagram with

Enzyme & Their Substrates Mode of Action Plantlet

Enzyme substrates and active sites chemical Vector Image
Enzyme Illustrations, RoyaltyFree Vector Graphics & Clip Art iStock
Enzyme

Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions
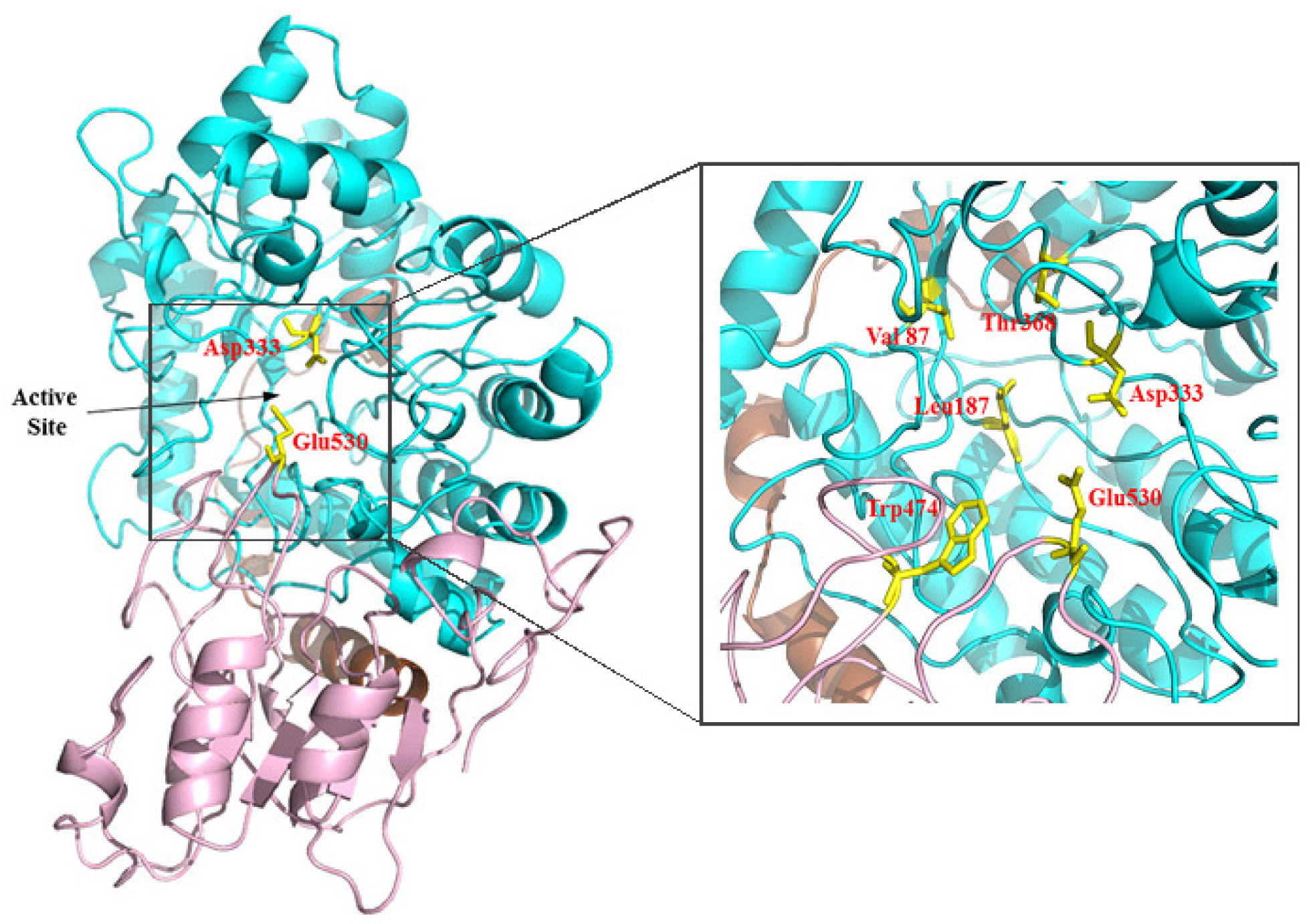
Enzymology Threedimensional structure of enzymes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-enzyme-structure-and-function-375555_v4-6f22f82931824e76b1c31401230deac8.png)
Structure and Function of an Enzyme
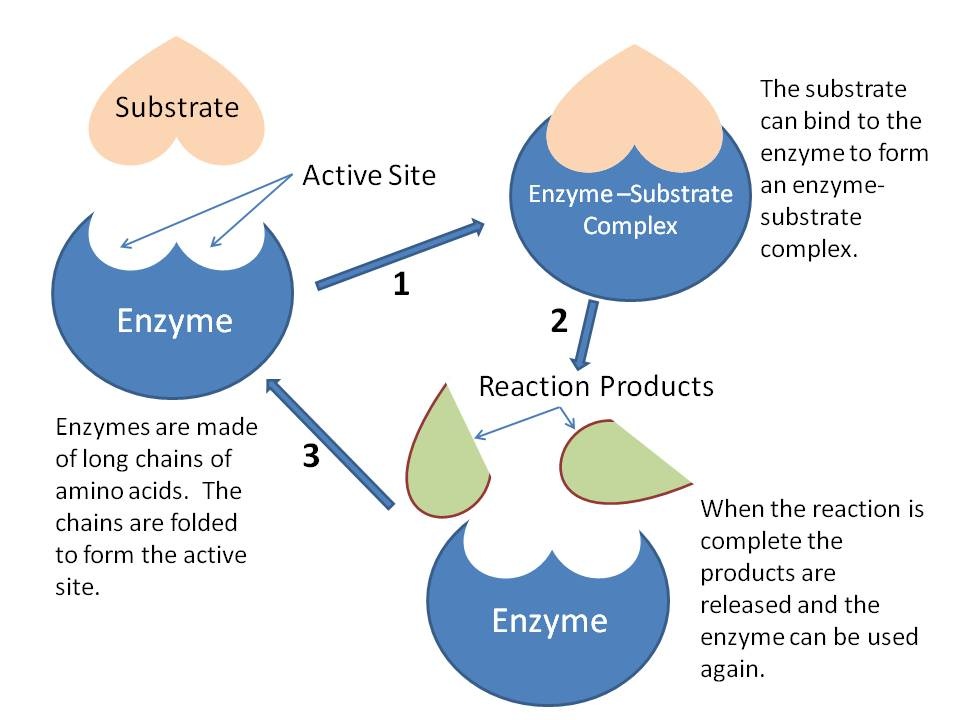
2.5 Enzymes BIOLOGY4IBDP
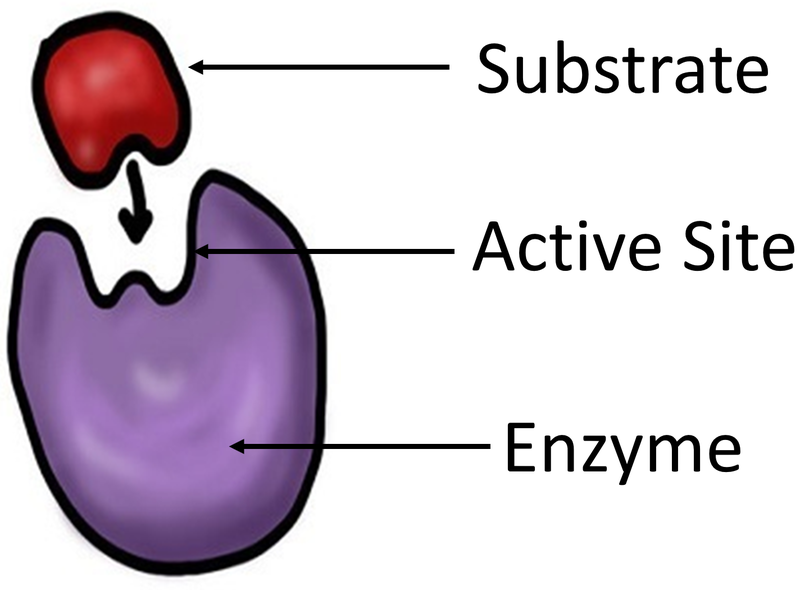
Enzyme Key Stage Wiki
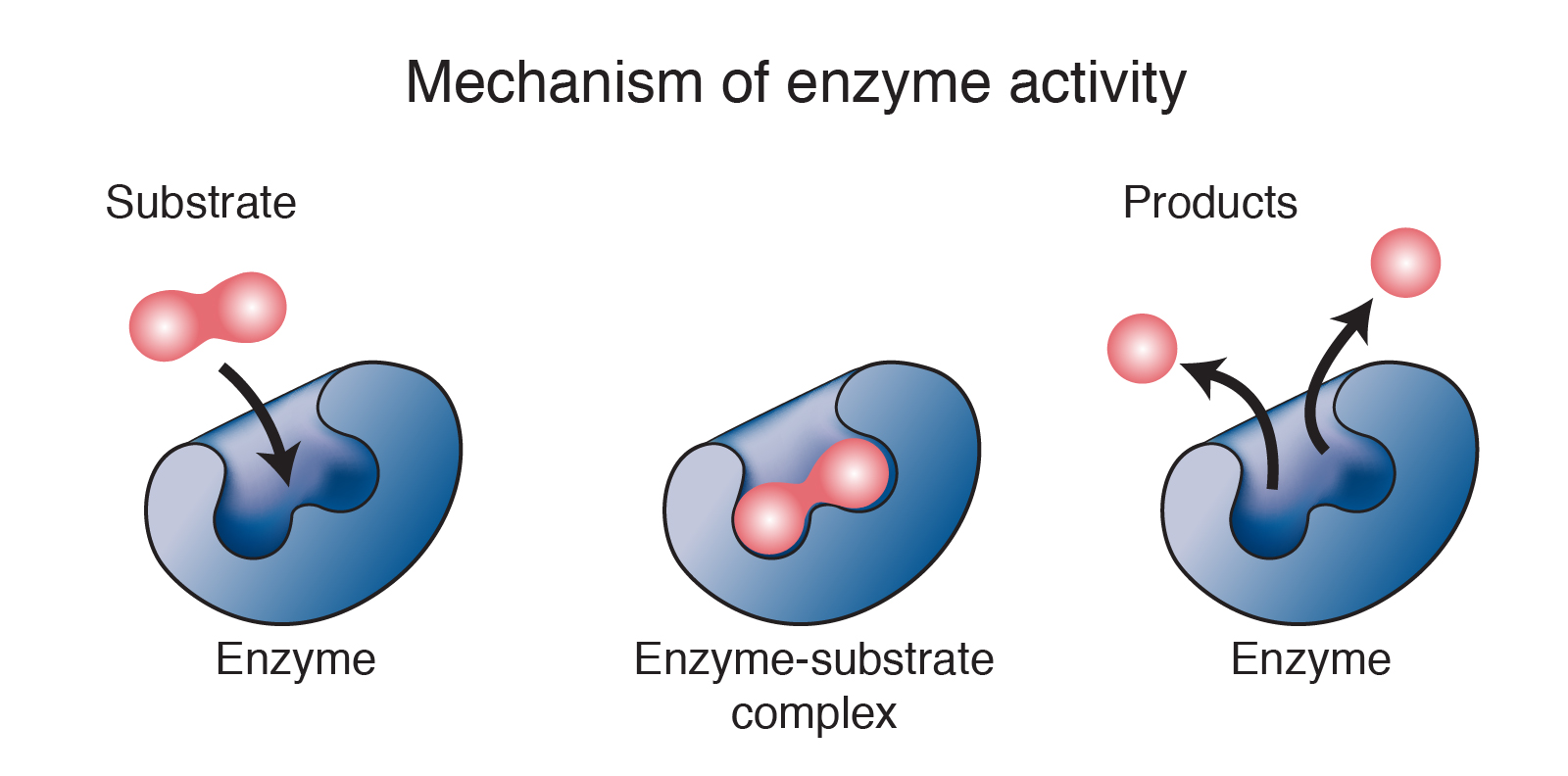
Web The Enzyme Binds Its Substrate At The Active Site To Form An Enzyme/Substrate Complex.
The Enormous Catalytic Activity Of Enzymes Can Perhaps Best Be Expressed By A Constant, K Cat, That Is Variously Referred To As The Turnover Rate, Turnover Frequency Or Turnover Number.this Constant Represents The Number Of Substrate Molecules That Can Be Converted To Product By A Single Enzyme Molecule.
Enzymes Are Proteins That Catalyze Biochemical Reactions By Lowering The Activation Energy Necessary To Break The Chemical Bonds In Reactants And Form New Chemical Bonds In The Products.
Schematic Drawing Of An Enzyme Reacting With Its Substrate.
Related Post:
