Drawing Of Smooth Muscle
Drawing Of Smooth Muscle - Smooth muscle cells or fibres of the longitudinal section #2. The table below compares the differences in the morphology of the three types of. Web human muscle system, the muscles of the human body that work the skeletal system, that are under voluntary control, and that are concerned with movement, posture, and balance. Web how to draw smooth muscle/muscle tissue diagram/how to draw smooth muscle easy.it is very easy drawing detailed method to help you.i draw the smooth muscle. It is very easy drawing detailed method to help you. Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as atp is freed for use by the myosin. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. Each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. Web smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle in function. Smooth muscle displays involuntary control and can be triggered via hormones, neural stimulation by the ans, and. Smooth muscle displays involuntary control and can be triggered via hormones, neural stimulation by the ans, and. Web smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle in function. Structure fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature. It is very easy drawing detailed method to help you. There are. Smooth muscle displays involuntary control and can be triggered via hormones, neural stimulation by the ans, and. Also, smooth muscle tissue is mostly cellular (and therefore more nuclei are present), whereas the connective tissue is mostly extracellular collagen fibers with fewer cells. The nucleus of smooth muscle cells or fibres of the longitudinal section #3. The nucleus of a smooth. Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as atp is freed for use by the myosin. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia, mitotically dividing to produce new cells. Web smooth muscle is one of three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and skeletal muscle. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by. Connective tissue surrounds the smooth muscle fibers or cells with fibroblasts #4. Web how to draw smooth muscle diagram/striated muscle diagram drawing. Structure fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature. Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as atp is freed for use by the myosin. The. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. Each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. Connective tissue surrounds the smooth muscle fibers or cells with fibroblasts #4. The two types have different locations in the body and have different characteristics. Diagrammatic view of three types. The table below compares the differences in the morphology of the three types of. The nucleus of a smooth muscle cell is elongated or oval that lies in the center of the cell. They are shown in figure below and described below. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. Web. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. Diagrammatic view of three types. And as multiunit smooth muscle. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; And as multiunit smooth muscle. Cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscle tissues. Web from the smooth muscle histology slide, you might identify the following important histological features. Web in this video i have shown the simplest way of drawing muscle drawing. Web how to draw smooth muscle diagram/striated muscle diagram drawing. Web how to draw smooth muscles and cardiac muscles step by step.it is very easy drawing detailed method to help you.i draw the smooth muscles with pencil on art. Connective tissue surrounds the smooth muscle fibers or cells with fibroblasts #4. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle (or skeletal muscle), smooth muscle,.. Web muscle cells, commonly known as myocytes, are the cells that make up muscle tissue. Web how to draw smooth muscles and cardiac muscles step by step.it is very easy drawing detailed method to help you.i draw the smooth muscles with pencil on art. Structure fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much. Its wavelike movements propel things through the bodily system, such as food through. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is capable of maintaining tone for extended periods and often contracts involuntarily. Web smooth muscle is one of three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and skeletal muscle. Smooth muscle cells (orange with purple nuclei) are embedded in the extracellular matrix, which is largely made of collagen and elastin fibers (green). Also, smooth muscle tissue is mostly cellular (and therefore more nuclei are present), whereas the connective tissue is mostly extracellular collagen fibers with fewer cells. Smooth muscle makes up the walls of hollow organs, respiratory passageways, and blood vessels. And as multiunit smooth muscle. Smooth muscle cells or fibres of the longitudinal section #2. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia, mitotically dividing to produce new cells. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle (or skeletal muscle), smooth muscle,. Diagrammatic view of three types. The two types have different locations in the body and have different characteristics. Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as atp is freed for use by the myosin. It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. Web smooth muscle is organized in two ways: Structure fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles, which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature.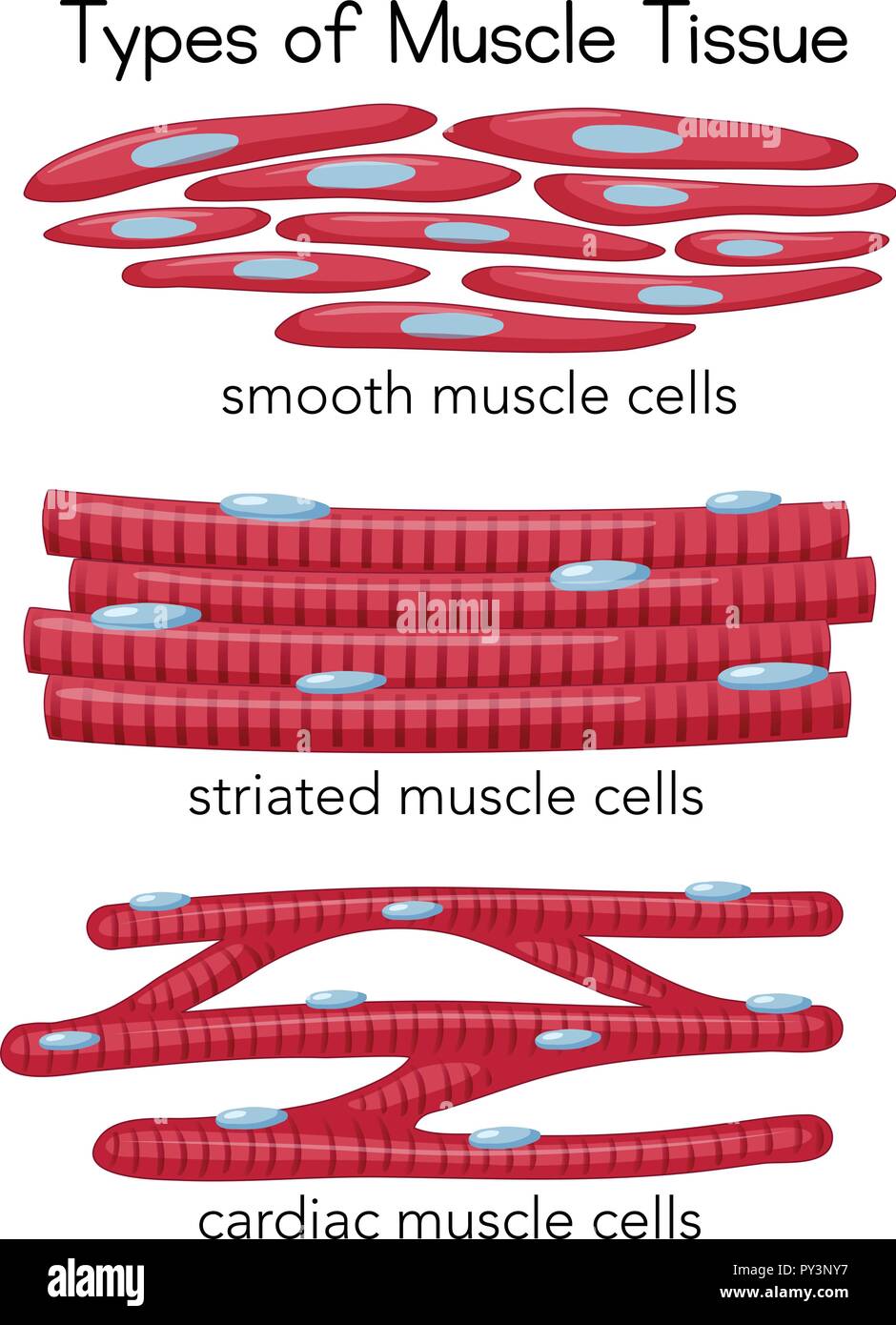
Smooth Muscle Diagram Drawing Notez On Nursing.... Tissues Muscle
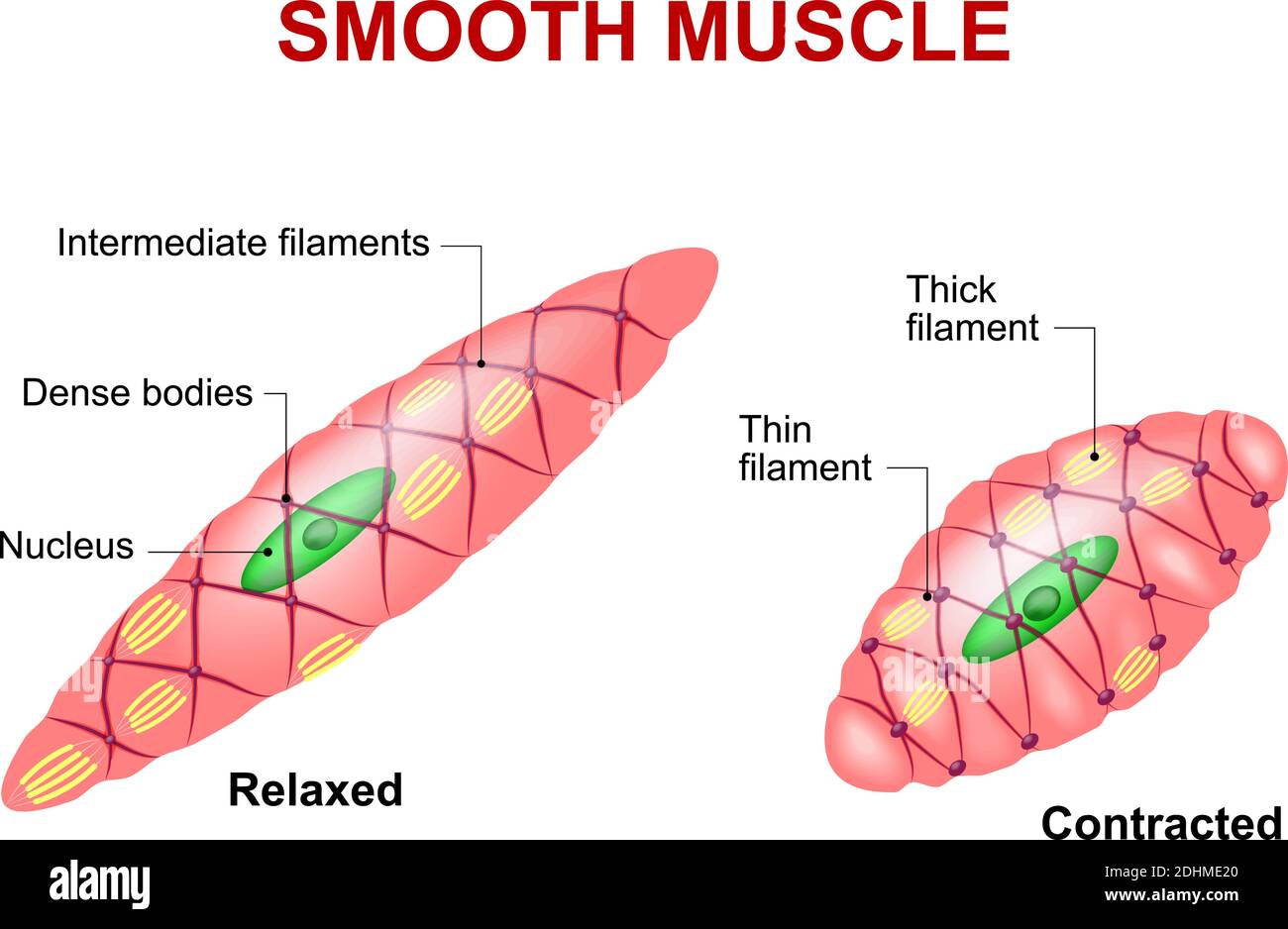
Smooth muscle tissue. Anatomy of a relaxed and contracted smooth muscle
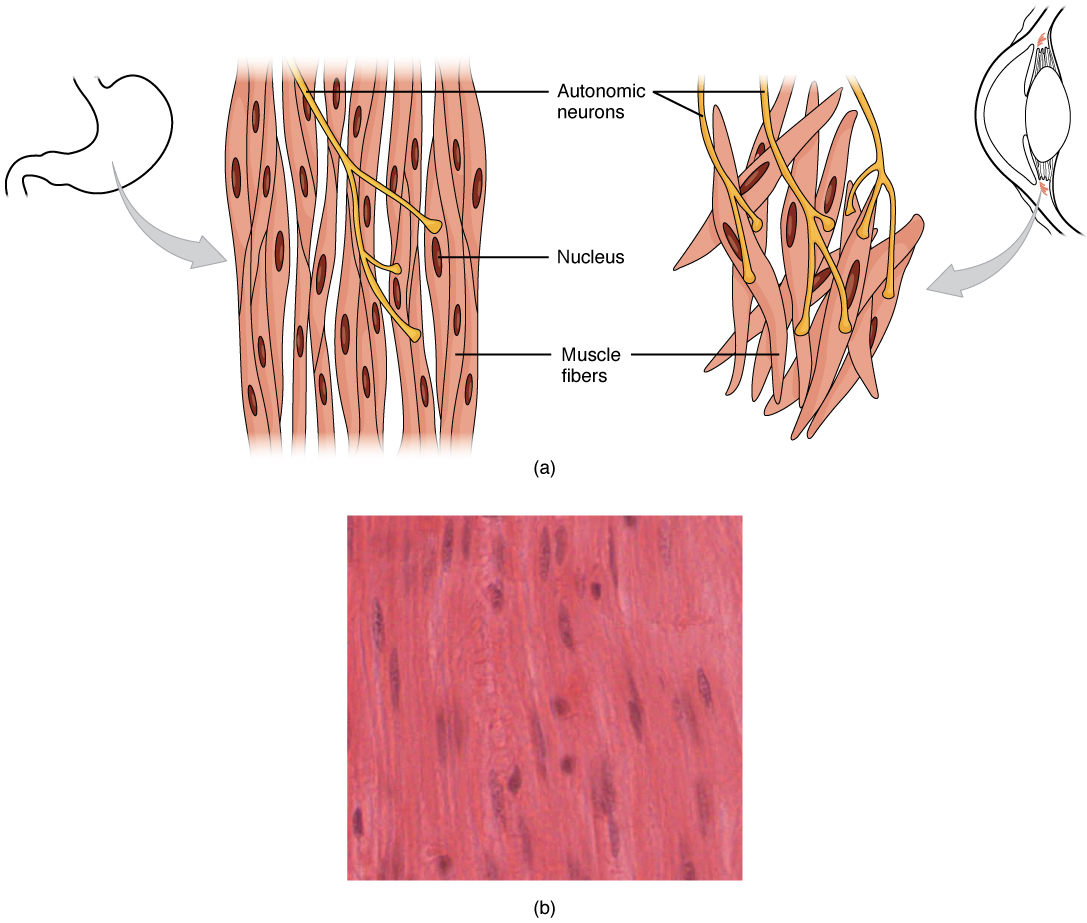
Smooth Muscle Anatomy and Physiology I Course Hero
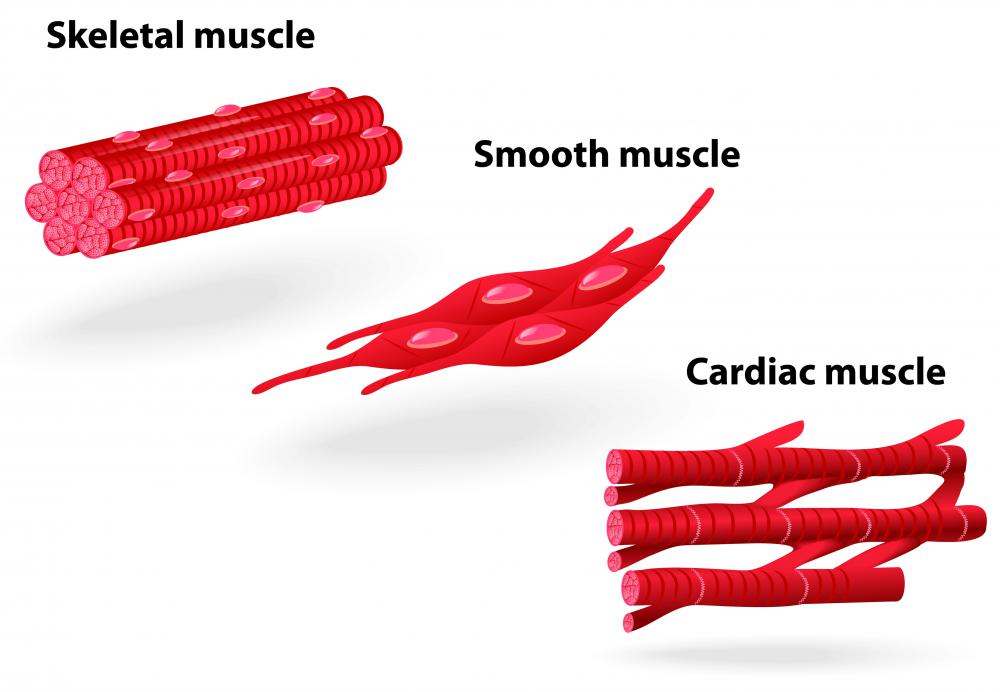
What is a Smooth Muscle Contraction? (with pictures)
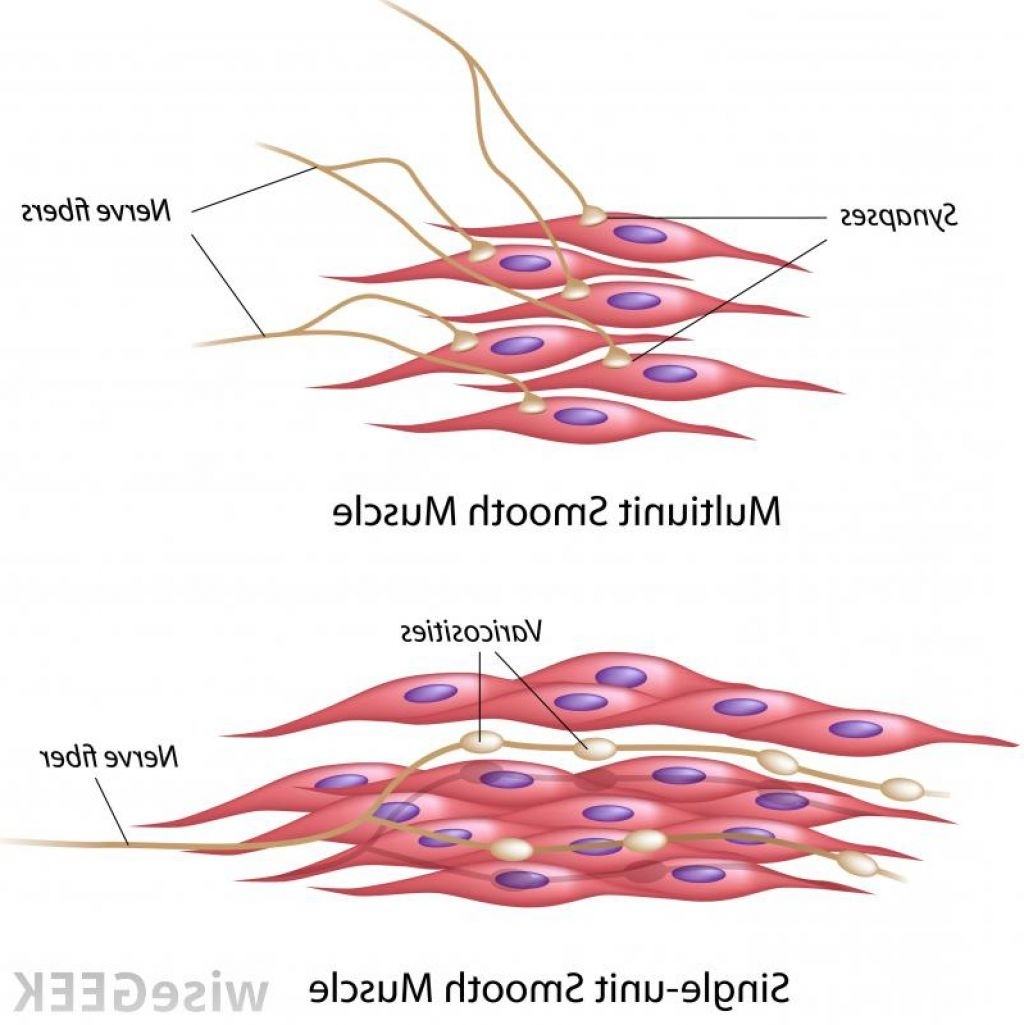
Smooth Muscle Diagram / Smooth muscle tissue. Smooth muscle tissue
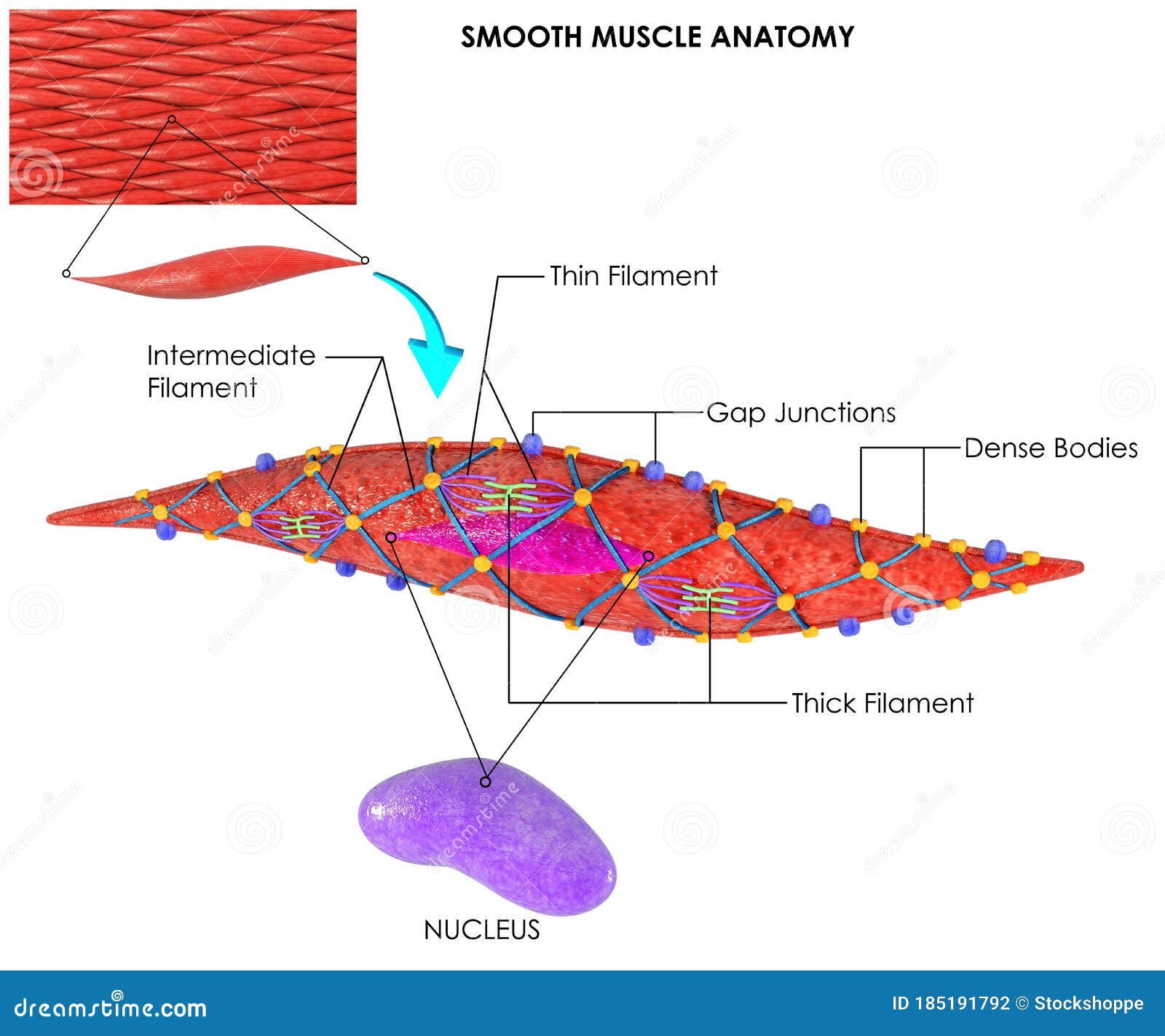
Smooth Muscle Anatomy for Biology Science Education Stock Illustration
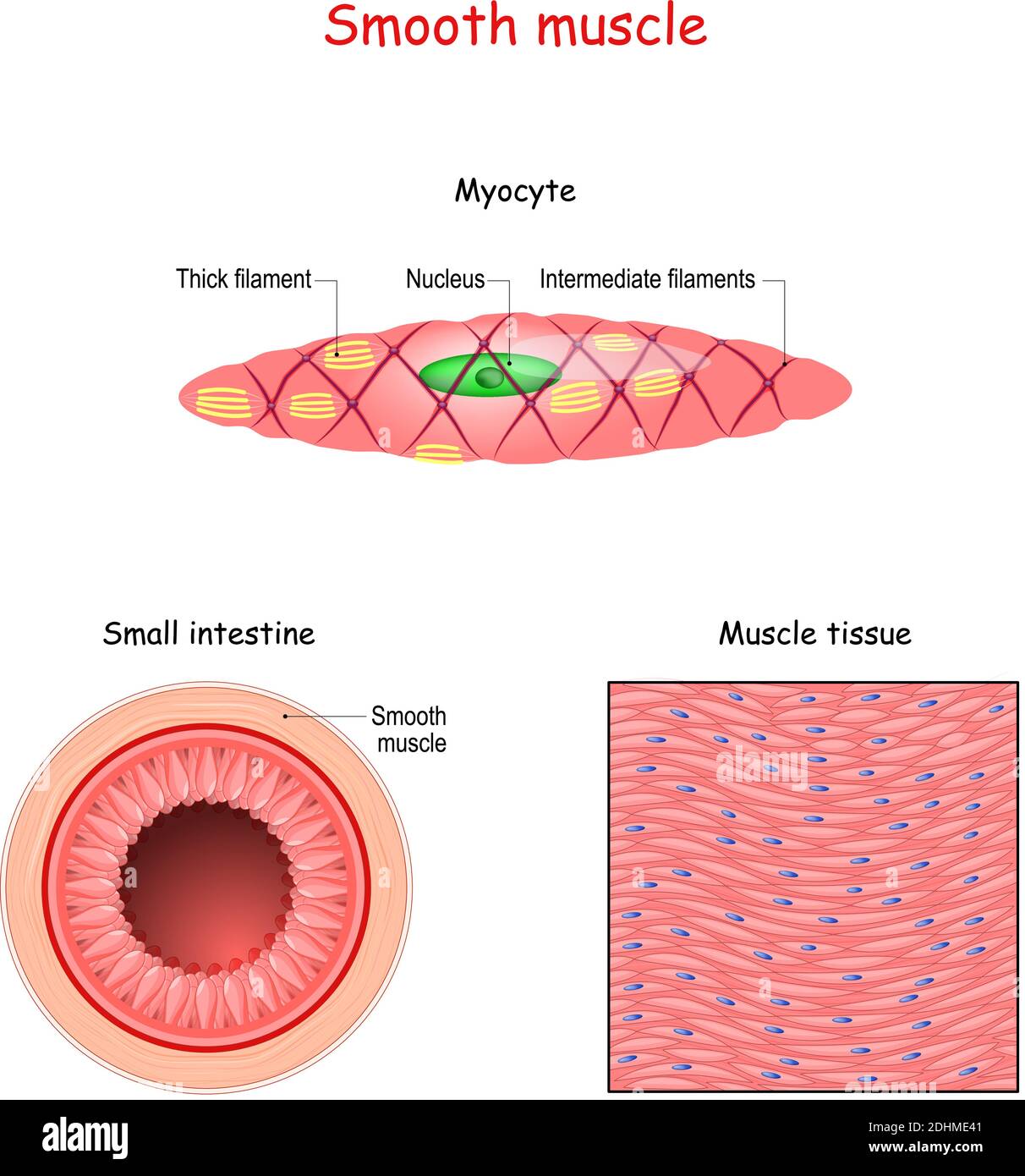
Structure of smooth muscle fibers. anatomy of Myocyte. Background of
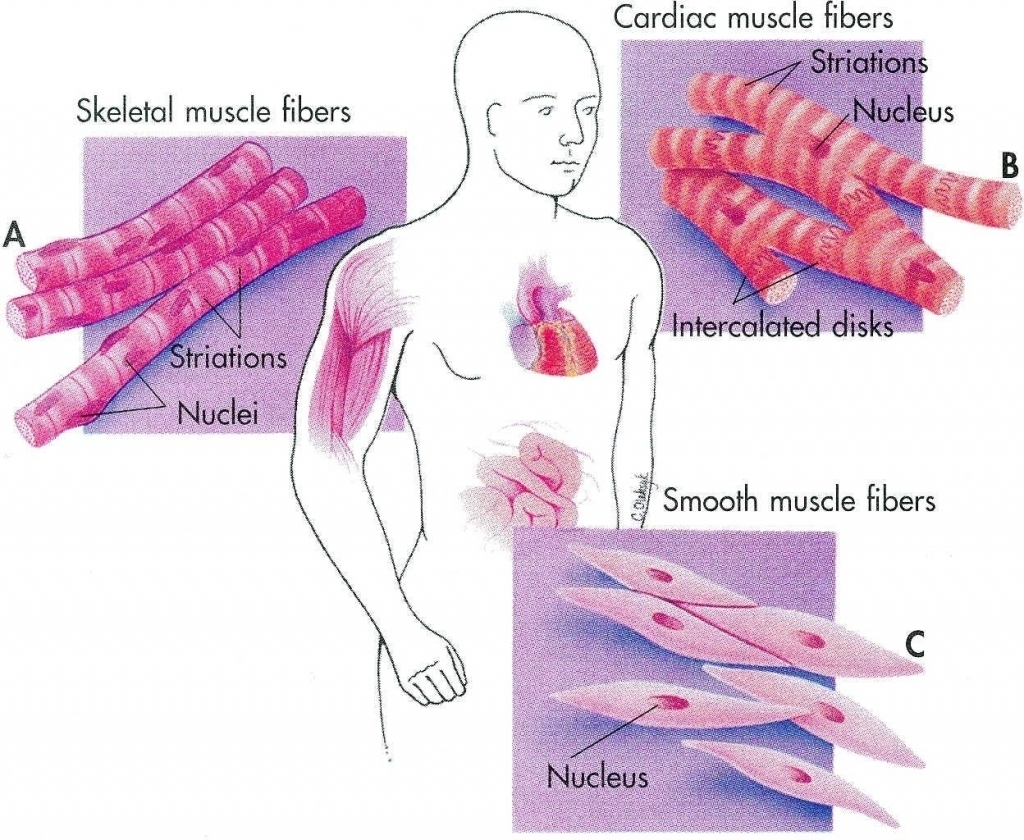
Smooth Muscle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
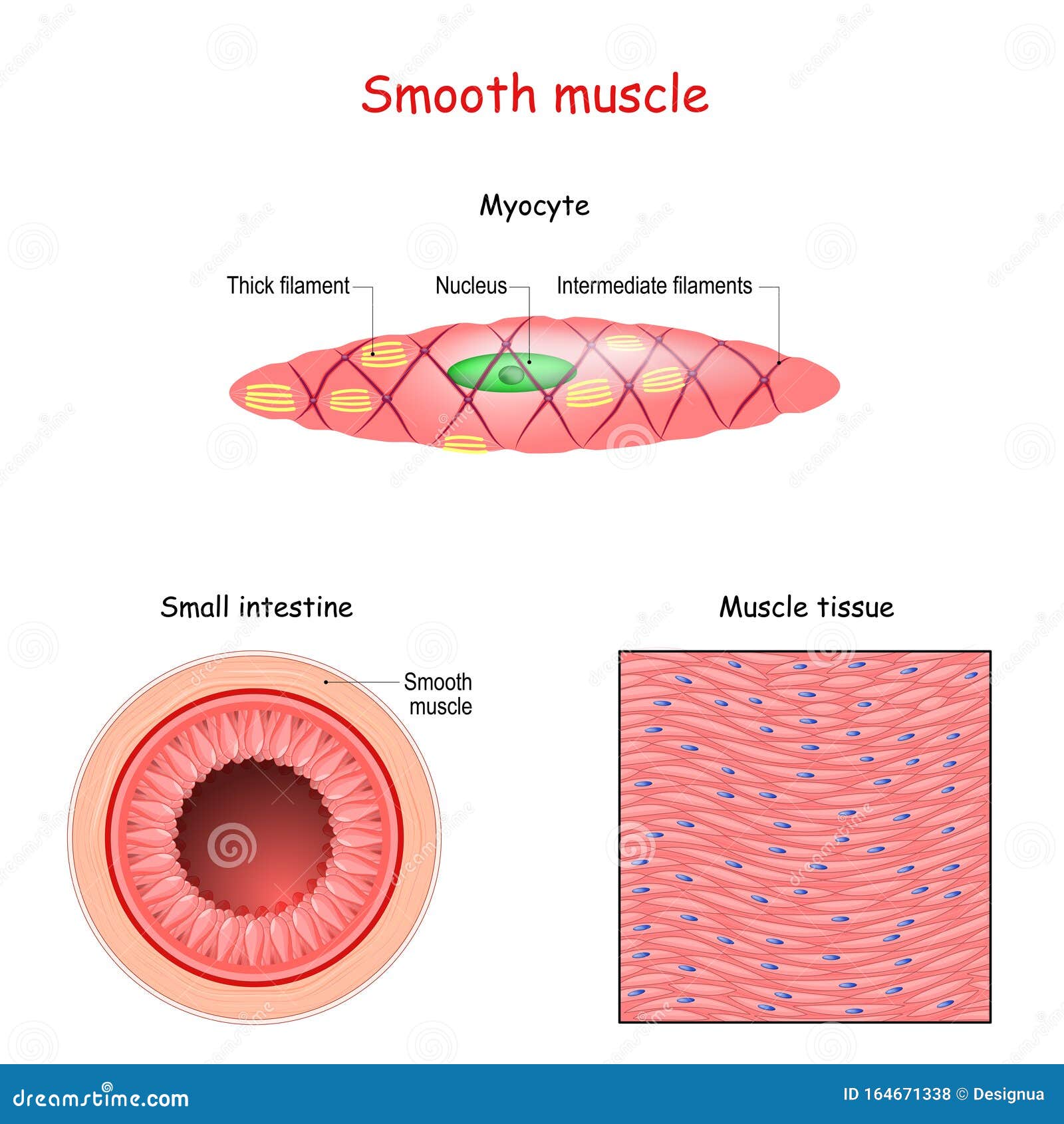
Smooth Muscle Anatomy

LM of a section through human smooth muscle tissue Stock Image P154
They Range From About 30 To 200 Μ M (Thousands Of Times Shorter Than Skeletal Muscle Fibers), And They Produce Their Own Connective Tissue, Endomysium.
They Range From About 30 To 200 Μ M (Thousands Of Times Shorter Than Skeletal Muscle Fibers), And They Produce Their Own Connective Tissue, Endomysium.
The Nucleus Of Smooth Muscle Cells Or Fibres Of The Longitudinal Section #3.
These Cells Have Fibers Of Actin And Myosin Which Run Through The Cell And Are Supported By A Framework Of Other Proteins.
Related Post: