Draw Shear And Moment Diagrams For The Beam
Draw Shear And Moment Diagrams For The Beam - Web r = span length of the bending member, in. In each problem, let x be the distance measured from left end of the beam. Web this problem has been solved! In each case, draw the shear and. Web draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam. 20 kn 40 kn/m cl 150 kn m 8 m 3 m prob. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web the shear diagram will plot out the internal shearing forces within a beam, or other body that is supporting multiple forces perpendicular to the length of the beam or body itself. 1) calculate support reactions 2). R = reaction load at bearing point, lbs. Establish the m and x axes and plot the values of the moment at the ends of the beam. Web this problem has been solved! Draw a free body diagram of the beam with global coordinates (x) calculate the reaction forces using. Web our calculator generates the reactions, shear force diagrams (sfd), bending moment diagrams (bmd), deflection, and stress of. P = total concentrated load, lbs. Web learn to draw shear force and moment diagrams using 2 methods, step by step. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the beam shown below. Web steps to construct shear force and bending moment diagrams. Draw a free body diagram of the beam with global coordinates (x) calculate the reaction forces using. Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the cantilevered beam. Web steps to construct shear force and bending moment diagrams. Shear force and bending moment diagrams are analytical tools used. Web this video is example 1 of how to draw shear and moment. Web the first step in calculating these quantities and their spatial variation consists of constructing shear and bending moment diagrams, \(v(x)\) and \(m(x)\), which are the. R = reaction load at bearing point, lbs. In each case, draw the shear and. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject. Draw a free body diagram of the beam with global coordinates. 20 kn 40 kn/m cl 150 kn m 8 m 3 m prob. Web steps to construct shear force and bending moment diagrams. Web write shear and moment equations for the beams in the following problems. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. B will be to write the and. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. 1) calculate support reactions 2). Web this video is example 1 of how to draw shear and moment diagram of beam. B will be to write the and. In each case, draw the shear and. Establish the m and x axes and plot the values of the moment at the ends of the beam. Web this video explains how to draw shear force diagram and bending moment diagram with easy steps for a cantilever beam loaded with a concentrated load. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core. A) determine the reactions at the supports. Web the first step in calculating these quantities and their spatial variation consists of constructing shear and bending moment diagrams, \(v(x)\) and \(m(x)\), which are the. When drawing shear and moment diagram, you first need to calculate the. We go through breaking a beam into segments, and then we learn about the relationships. Web learn to draw shear force and moment diagrams using 2 methods, step by step. Web for example, if w(x) is uniform, v(x) will be linear. Web this problem has been solved! P = total concentrated load, lbs. In each problem, let x be the distance measured from left end of the beam. Web draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam. Web the shear diagram will plot out the internal shearing forces within a beam, or other body that is supporting multiple forces perpendicular to the length of the beam or body itself. In each problem, let x be the distance measured from left end of the beam. Web the first. Web this is an example problem that will show you how to graphically draw a shear and moment diagram for a beam. P = total concentrated load, lbs. 20 kn 40 kn/m cl 150 kn m 8 m 3 m prob. When drawing shear and moment diagram, you first need to calculate the. 1) calculate support reactions 2). A) determine the reactions at the supports. Shear force and bending moment diagrams are analytical tools used. Establish the m and x axes and plot the values of the moment at the ends of the beam. In each problem, let x be the distance measured from left end of the beam. Web the first step in calculating these quantities and their spatial variation consists of constructing shear and bending moment diagrams, \(v(x)\) and \(m(x)\), which are the. Web this problem has been solved! Web for example, if w(x) is uniform, v(x) will be linear. We go through breaking a beam into segments, and then we learn about the relationships between. R = reaction load at bearing point, lbs. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. In general the process goes like this:
Solved Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam

Drawing Shear and Moment Diagrams for Beam YouTube
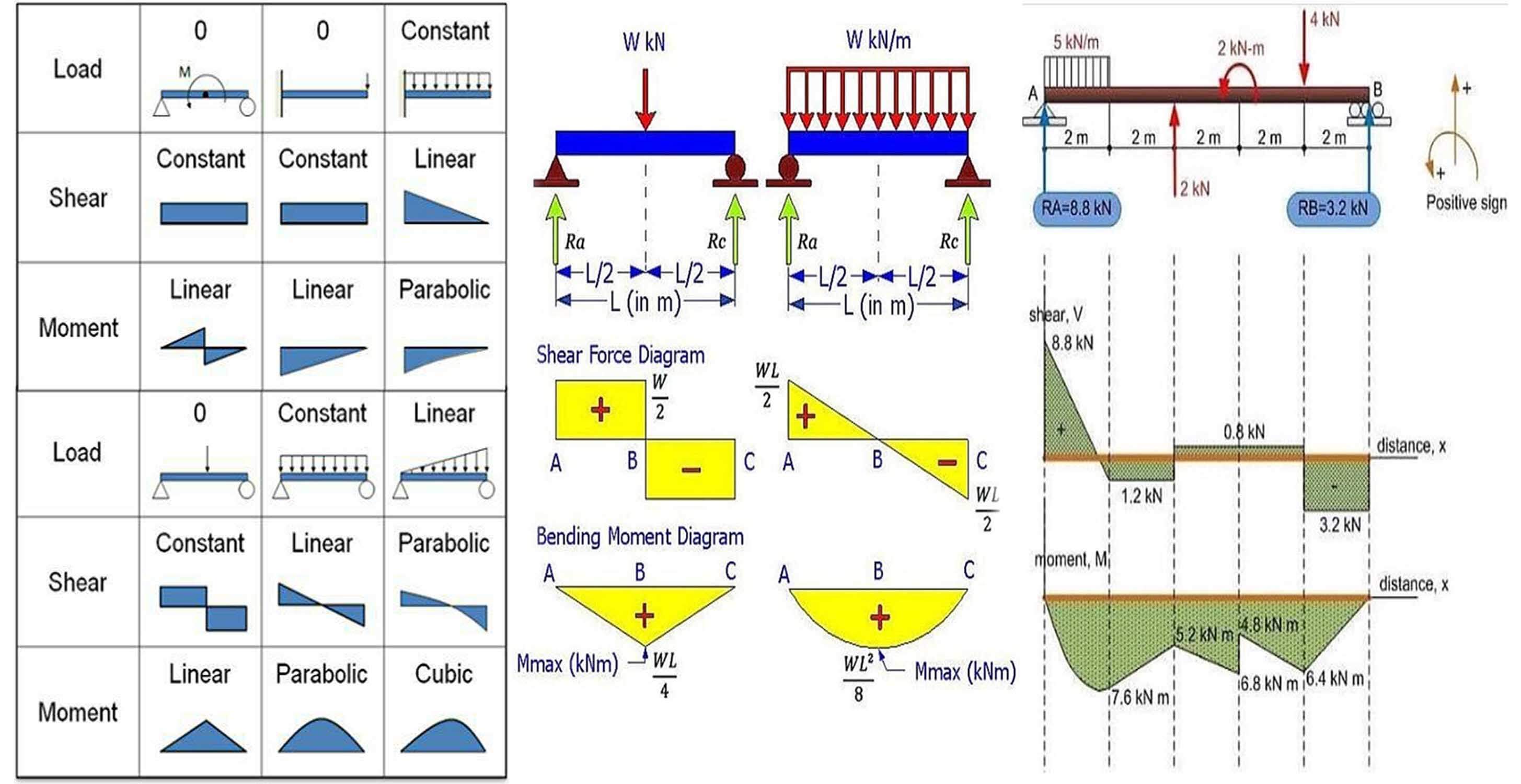
Learn How To Draw Shear Force And Bending Moment Diagrams Engineering
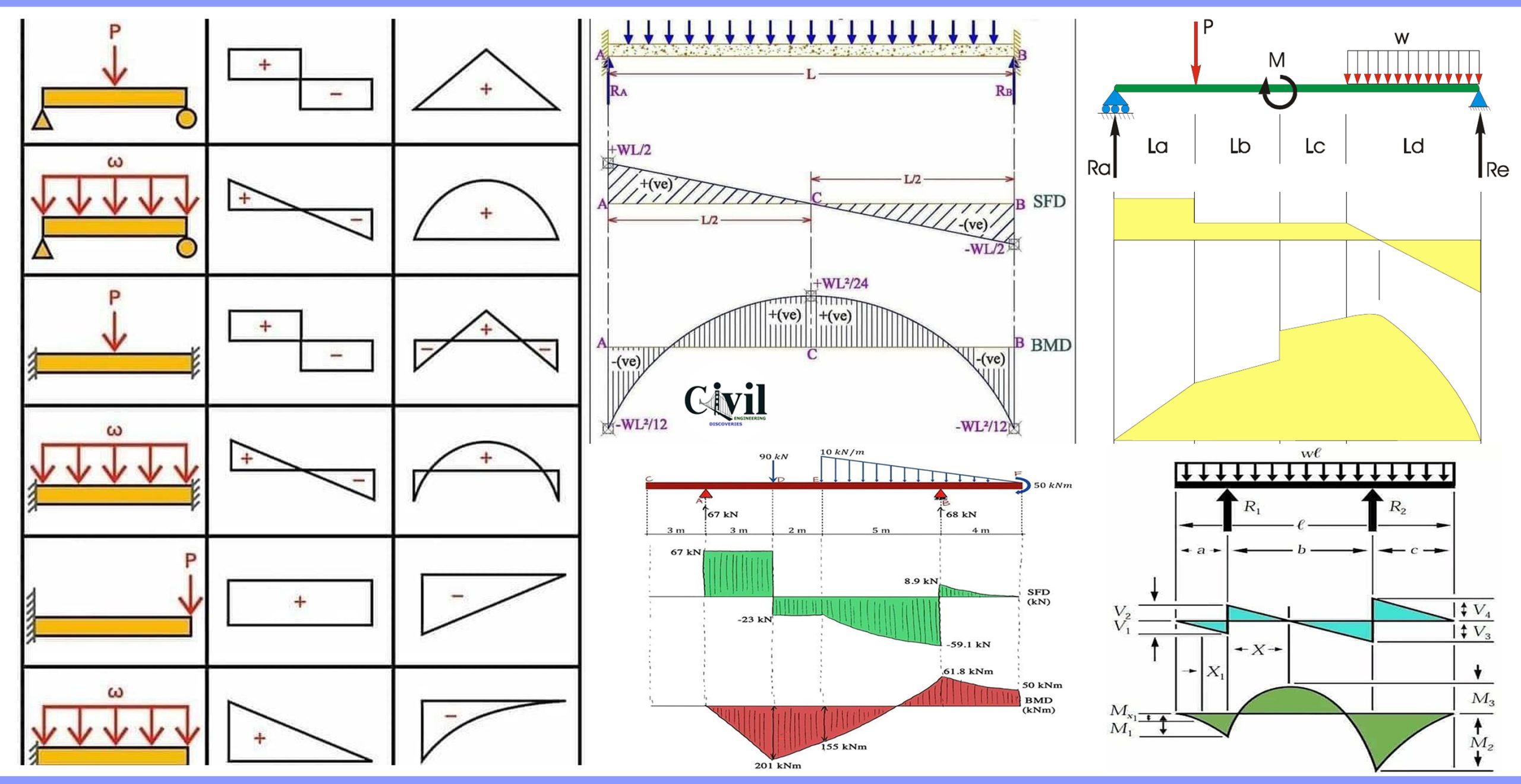
Brief Information About Shear Force And Bending Moment Diagrams

Shear force and bending moment diagrams for beams pdf
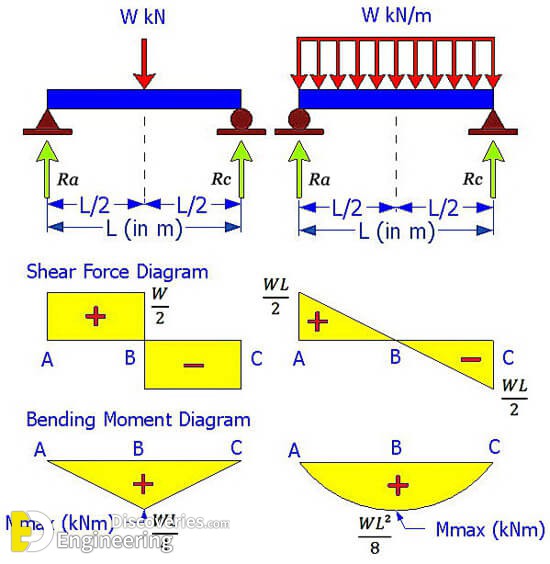
Learn How To Draw Shear Force And Bending Moment Diagrams Engineering

Bending moment and shear force diagram of a cantilever beam
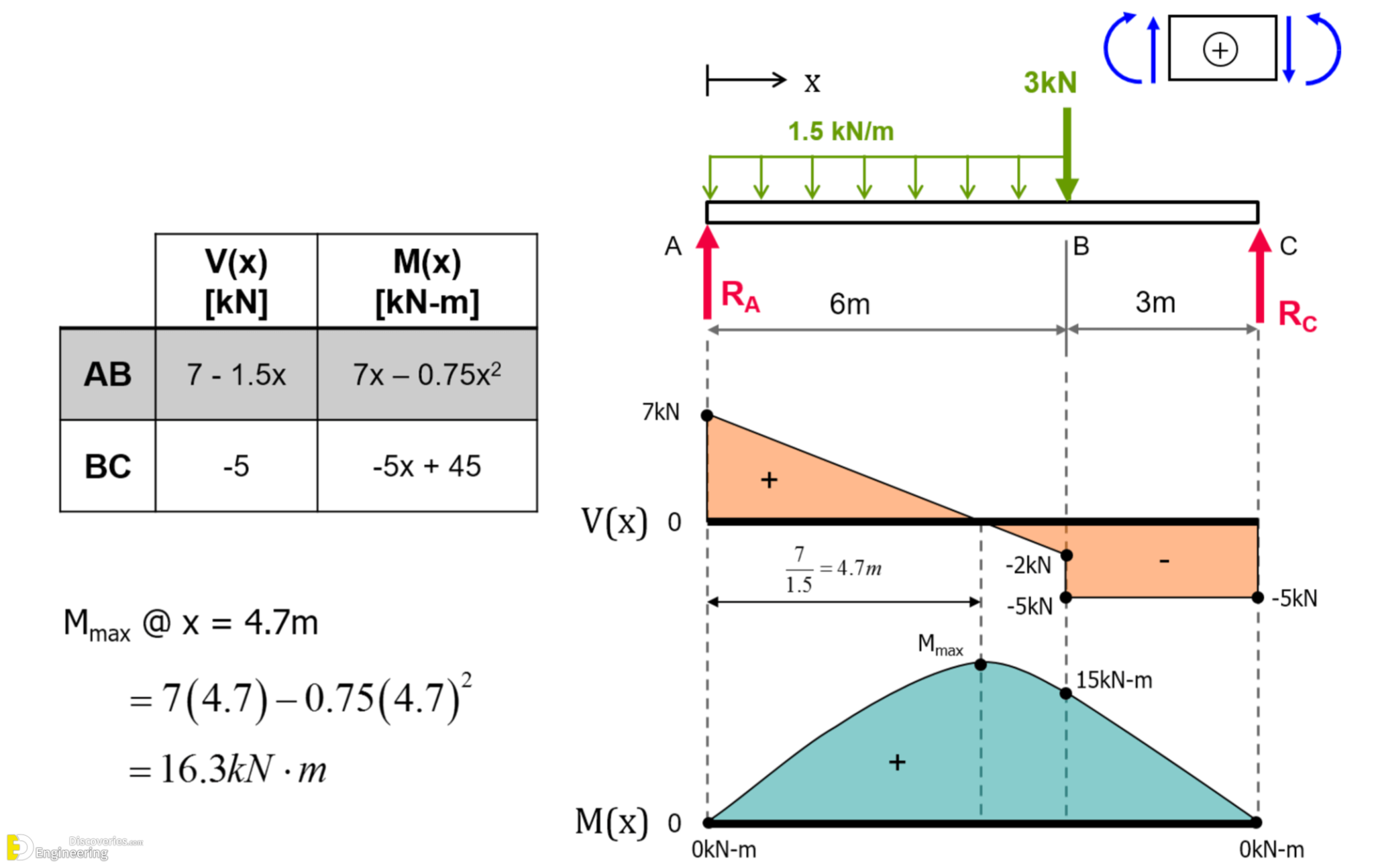
Learn How To Draw Shear Force And Bending Moment Diagrams Engineering
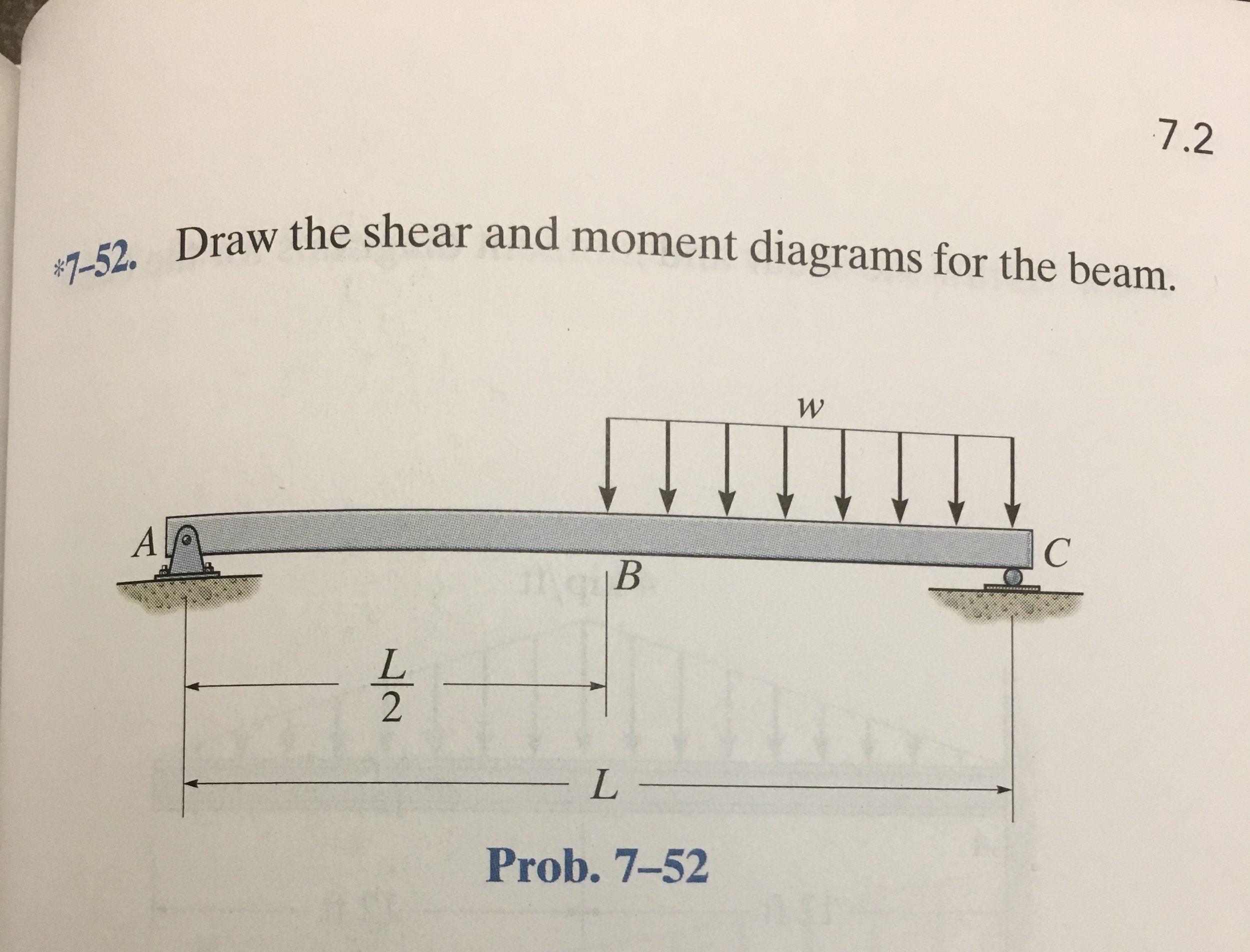
Solved Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam.
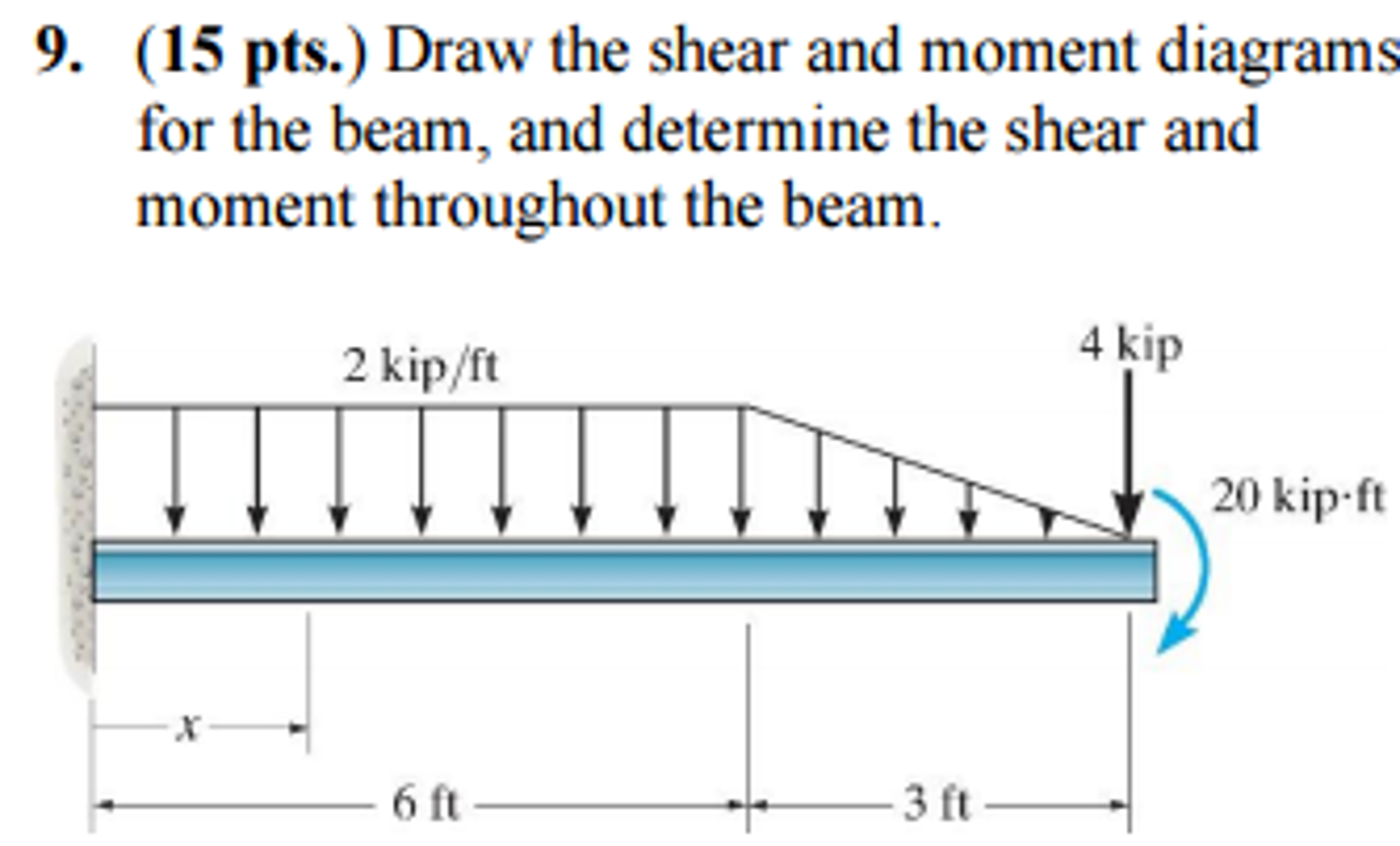
Solved Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam, and
B Will Be To Write The And.
Web Learn To Draw Shear Force And Moment Diagrams Using 2 Methods, Step By Step.
Web This Problem Has Been Solved!
Web Write Shear And Moment Equations For The Beams In The Following Problems.
Related Post: